Your Specialist For Die-Cutting EMI Gaskets
- Over 20 years of Die Cutting experience
- Top-Notch Die-Cutting EMI Gaskets Production Standards
- ISO14001 Certified Die-Cutting EMI Gaskets Production
- Various materials available
- Product Details
- Application Overview
- Material Insights
- EMI gaskets made with cured silicone or fluorosilicone rubber, these provide excellent EMI/RFI shielding.
- The EMI gaskets offer environmental sealing and insulation in addition to EMI protection.
- EMI Gaskets perform across a wide temperature range from -55°C to +200°C.
- Fluorosilicone materials are ideal for harsh environments like fuel and solvent exposure.
- EMI Gaskets meet UL94 V-0 flame resistance standards for added safety.
Jiepu, with extensive die-cutting experience, has worked with EMI Gaskets in various industries to help reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI).
In aviation, EMI Gaskets protect critical electronic systems, like navigation and communication equipment, ensuring flight safety. In military equipment, they safeguard sensitive communication and radar systems from interference.
In medical electronics, they ensure that imaging and monitoring devices work correctly in electromagnetic environments. For industrial controls, they protect panels and sensors from EMI in factory settings.
EMI Gaskets are used in high-precision test equipment to prevent interference from affecting results and in communication systems to maintain clear signals. In cars, they reduce EMI in control systems, improving reliability and safety.
These gaskets are also used in the casings of consumer electronics like phones and laptops, ensuring the devices remain shielded from EMI.
Jiepu, with years of die-cutting expertise, presents the characteristics of various EMI Gasket materials.
Conductive silicone rubber gaskets are made from silicone rubber filled with conductive particles. They provide excellent shielding while also offering sealing and insulation, making them suitable for harsh environments with a temperature range from -55°C to +200°C.
Fabric-over-foam (FoF) gaskets combine conductive fabric with foam. The foam offers flexibility, while the fabric provides EMI shielding, making it ideal for applications needing both protection and compression.
Metal foils, like copper, aluminium, and tin, are highly conductive and reflect or absorb electromagnetic waves, offering excellent shielding in thin, easy-to-install forms.
Conductive/insulating rubber and foam gaskets combine the flexibility of foam with conductive particles to provide effective EMI shielding and environmental sealing.
Metal mesh dipped in synthetic rubber or silicone combines the conductivity of metal with the flexibility of rubber, offering reliable EMI shielding in various installation environments.
Flexible ferrites are made from polymer sheets filled with magnetic particles, ideal for high-frequency applications and easy to install with adhesives.
Custom Die-Cut Solutions with EMI Gaskets
Morbi iaculis at quam vel faucibus. Ut semper ipsum ex, quis aliquet justo pretium a. Suspendisse scelerisque metus augue, a interdum leo iaculis sed. Vivamus sit amet nunc odio. Duis vel pulvinar dolor, at lacinia tellus.
Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Suspendisse lacinia quam a elit lobortis tempor
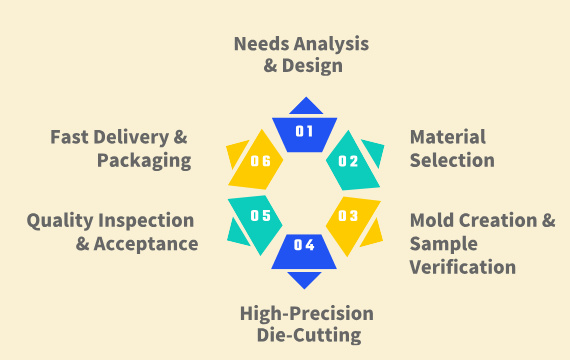
Precision Die-Cutting Process for EMI Gaskets
At Jiepu, we frequently use precise die-cutting processes for Foil Heat Shields, ensuring accurate shapes and reliable performance. The process begins with material preparation, where high-quality aluminium foil is inspected to ensure no defects like holes or creases, as these impact heat resistance.
Next, we design a custom mould based on the shield’s thickness and size. Using techniques like flatbed cutting for thin foils or rotary cutting for larger pieces, we achieve clean, precise cuts. Additional steps, such as punching holes or shaping, ensure the final product meets specific requirements.

Certified Die-Cutting Services with Foil Heat Shields
We provide high-quality die-cutting services, supported by ISO 9001 for quality, ISO 14001 for environmental care, and IATF 16949 for the automotive industry. These certifications ensure that our services meet international standards, delivering reliable, efficient, and environmentally responsible solutions.
Our Foil Heat Shields are made from high-performance materials like aluminium foil, designed to reflect heat and protect equipment from overheating. We offer custom sizes and fast sample delivery, meeting the unique needs of our clients.
Find Your Perfect Die Cutting Materials

Easy Steps for EMI Gaskets Samples and Quotation
At Jiepu, we simplify the process of requesting samples and getting quotes for EMI Gaskets. Here’s how it works:
- Drawing Confirmation: We check your 2D drawings to ensure accurate production. Using commonly available materials helps us avoid delays.
- Process Review: We analyse the production steps to make sure they are efficient and practical. Complex parts? No problem—we’ll plan for precision.
- Quick Quotation: Quotes are prepared within 24 hours, based on order size and complexity. Larger orders may qualify for refunded tooling fees.
- Sample Production: Samples are crafted within 72 hours using detailed specifications. Clear communication ensures a perfect fit.
- Quality Inspection: Each sample undergoes thorough testing, complete with a measurement report.
- Sample Delivery: We provide full documentation, including certifications, drawings, and inspection reports, for smooth approval.
- Mass Production: Once the sample is approved, production begins with ongoing quality checks for a flawless outcome.
- Timely Delivery: Final products are packed and shipped promptly, with full after-sales support to meet your needs.
We handle every detail, ensuring accurate EMI Gaskets samples and quotes with no hassle. Let’s work together!

Shielding gaskets, also called EMI gaskets, are designed to block electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (RFI) from passing through gaps in devices. Here’s why they’re special:
- High Conductivity: Made with materials like metal, conductive silicone, or rubber, they effectively block electromagnetic waves.
- Environmental Sealing: They also keep out dust, moisture, and contaminants, protecting sensitive equipment.
- Works in Extreme Temperatures: These gaskets handle both very cold and very hot conditions, making them reliable everywhere.
- Flame Resistance: Some meet strict safety standards like UL94 V-0, ensuring they’re fire-resistant.
- Flexible Options: Available as rings, profiles, flat gaskets, O-rings, or sheets, they suit a range of applications.
- Adhesive Backing: Some have sticky layers for easy installation in grooves or interfaces.
- Reduces EMI: They lower interference, improving device reliability and reducing false operations.
- Easy to Cut and Install: Simple to handle, these gaskets can be shaped into complex forms as needed.

EMI sealing pads are used in lots of different areas to stop unwanted electromagnetic interference (EMI). Here are some common examples:
- Car systems: They protect car electronics like control units and safety systems from EMI.
- Aircraft electronics: In planes, they reduce interference in sensitive equipment, making sure everything works properly.
- Communication systems: Used in mobile phone towers and other communication equipment to improve signal quality and reduce EMI.
- Computers and electronics: They help shield computers and fast electronic devices from interference.
- Medical devices: Found in machines like MRI scanners and pacemakers, they protect against EMI to ensure patient safety.
- Connectors: These pads are used around connectors in electronic devices to stop EMI and keep them sealed.
- Industrial equipment: In factories, they reduce interference in control systems, ensuring everything works smoothly.
- Test equipment: Used in testing devices to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Military equipment: Protects military electronics from interference, ensuring secure communications.
- Consumer electronics: Found in things like smartphones, laptops, and game consoles to block EMI and meet safety standards.
- Wireless communication: In devices like Wi-Fi routers, they help improve signal quality and prevent static or interference.

To test if an EMI sealing pad works properly, there are several key things we check:
- Bounce-back test: This checks how well the pad can return to its original shape after being compressed. The pad should bounce back quickly after pressure is released, which helps ensure that the device continues to be protected from interference after it’s opened or closed.
- Environmental tests: We test the pad’s performance under different conditions, like low temperatures, heat, vibrations, salty air, and humidity. These tests help make sure the pad lasts and works well in extreme conditions.
- Shielding effectiveness: This measures how well the pad blocks electromagnetic interference. It’s tested by comparing the amount of interference with and without the pad, using special equipment to measure things like voltage or signal strength.
- Flange coaxial test: This test is done using a special device that creates a consistent field to measure how well the pad blocks waves of electromagnetic interference in a certain frequency range (30 MHz to 3 GHz).
- Sealing performance test: This test checks how well the pad seals, making sure no leaks can occur when the pad is under pressure. It’s tested with equipment that calculates the amount of leakage to ensure the pad provides a strong seal.

The performance of an EMI sealing gaskets can change with temperature in several ways:
Hardening and compression changes: When the temperature drops, the material of the pad hardens, which means it doesn’t compress as much under pressure. This is more noticeable in very cold conditions. For example, at -253°C (20 K), the pad compresses much less than it would at room temperature (around 20°C or 293 K).
Size changes: Lower temperatures can also cause the size of parts like joints and connectors to change. This might create gaskets between the pad and the parts it’s sealing, which can lead to leaks, especially in very cold conditions.
Sealing pressure changes: The pressure at which the pad seals can also change with temperature. For example, at very low temperatures, the pad’s sealing pressure is usually lower than at room temperature. This can happen because the parts around the pad shrink, leaving more space for the pad to compress less.
Leakage rate: At very low temperatures, the gasket might seal less effectively because its contact area becomes smaller, and the gas can flow more easily through tiny gaps, leading to higher leakage rates compared to normal temperatures.
Adaptability to different environments: Some EMI sealing gaskets, like the GORE® SMT EMI shielding grounding pads, have been tested in extreme conditions (very cold, hot, humid, and with vibrations) and have shown stable performance in these environments.
Operating temperature range: Different pads are designed to work within specific temperature ranges, such as -40°C to 150°C or -40°C to 160°C, meaning they can maintain their performance over a wide range of temperatures.
In short, the performance of an EMI sealing pad can change significantly at different temperatures, especially in very cold environments. These changes can affect how well the pad seals and blocks EMI. So, when choosing the right pad, it’s important to consider how it will perform at the temperature it will be used in.

EMI shielding gaskets don’t necessarily fail completely in extremely low temperatures, but their performance does change. Here are a few important points:
- Material hardening and compression changes: As the temperature drops, the material of the shielding gasket becomes harder, which means the gasket doesn’t compress as much under the same pressure. For example, at -253°C (20 K), the gasket compresses less than it would at room temperature (about 20°C).
- Size changes: Lower temperatures can cause parts like joints to shrink, which can create gaps and lead to higher leak rates.
- Leakage rates: In extremely low temperatures, the material gets harder, which reduces the sealing width and can make it easier for leaks to happen. This is due to changes in the material’s properties, such as lower viscosity of gases, making them flow more easily through small channels.
- Adaptability: Some EMI shielding gaskets, like the GORE® SMT EMI shielding ground gaskets, have been tested in extreme environments, including low temperatures of -65°C, and show stable performance.
- Elasticity changes: Tests show that the gasket’s elasticity increases as the temperature drops, meaning the material becomes stiffer.
- Leakage predictions at low temperatures: Research shows that as temperature decreases, the gasket’s ability to compress reduces, and structural changes can lead to gaps, which increases leakage.
So, EMI shielding gaskets might not completely fail in extremely low temperatures, but their performance can be affected. These changes include harder materials, less compression, size changes, and increased leakage. So, when choosing an EMI shielding gasket, it’s important to think about how it will perform in specific temperature conditions.
![]()
No, EMI gaskets are not always silicone. While silicone is common for its flexibility and conductivity, other materials are also used, such as:
- Metal (e.g., copper, aluminum) for high shielding.
- Conductive rubber with particles for shielding.
- Conductive foam for light, flexible uses.
- Conductive fabrics like stainless steel fiber.
- Thin films (e.g., copper, aluminum) for flexible layers.
- Composites combining materials for balance.
- Conductive adhesives for sealing and shielding.
- Metal mesh for moderate shielding.
The material depends on shielding needs, environment, stress, and cost. Silicone stands out for durability and temperature resistance but isn’t the only option.

It’s called EMI gasketing because it helps manage electromagnetic interference (EMI) while also working like a regular gasket. Here’s the simple idea:
- What’s EMI?
EMI is unwanted energy from electronics that can mess up other devices nearby. Think of it like noise that disturbs a clear radio signal. - What does a gasket do?
A gasket seals gaps between parts. In this case, an EMI gasket also helps electricity flow between surfaces, creating a shield that blocks interference. - How does it help?
By stopping EMI from getting in or out of a device, the gasket keeps electronics working smoothly and avoids signal problems.
So, the name “EMI gasketing” combines these two jobs: sealing and shielding. Simple as that!


















