Die-cutting materials play a crucial role in creating precise components found in products we use daily, such as smartphones, cars, and home appliances. These materials not only ensure durability and reliability but also enhance the overall efficiency of the products.
Jiepu, a leading company with 22 years of expertise in this field, collaborates with renowned global brands like Samsung, Apple, and Honda to deliver high-quality die-cutting solutions. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the various types of die-cutting materials available, their unique features, and how they are used in different industries to meet specific needs.
Content
Types of Die-Cutting Materials

1. Adhesive Tapes
What They’re Like: Sticky, flexible, and able to handle heat and chemicals.
Examples: VHB Tape, conductive tape, Foil Tapes, EMI Shielding Tapes, Thermal Tapes, Hook and Loop etc.
Uses: Sticking parts in electronics, car interiors, and labels.
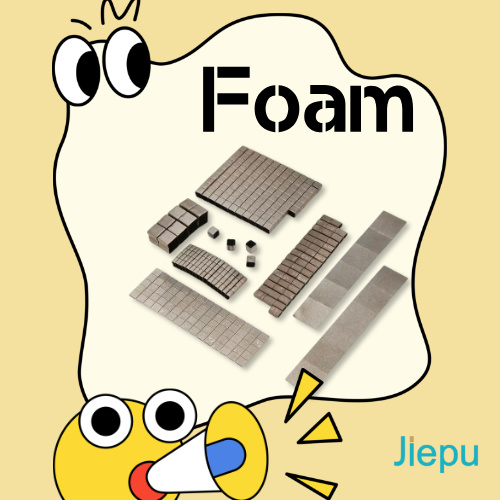
2. Foam Materials
What They’re Like: Lightweight, soft, and good at absorbing shocks.
Examples: EMI Shielding Foam, Conductive Foam, PU foam, Neoprene Foam, Silicone Foam.
Uses: Packaging, reducing vibration in devices, and sealing gaps.
3. Silicone Materials
What They’re Like: Handles high and low temperatures, lasts long, and is safe for food and electronics.
Examples: Thermal Conductive Silicone, BISCO Silicones.
Uses: Medical tools, food containers, and insulating electronics.

4. Rubber Materials
What They’re Like: Stretchy, tough, and resistant to oil and chemicals.
Examples: Rubber Sheet, Silicone Rubber, Urethane Rubber.
Uses: Car parts, seals, and industrial gaskets.

5. Gaskets
What They’re Like: Strong, good at sealing, and resistant to pressure.
Examples: EMI Gaskets, Felt.
Uses: Sealing pipes, machinery, and flanges.

6. Films
What They’re Like: Thin, light, transparent, and flexible.
Examples: Mylar Film, PET film, PVC film, PE film.
Uses: Packaging, screen protection, and optical parts.
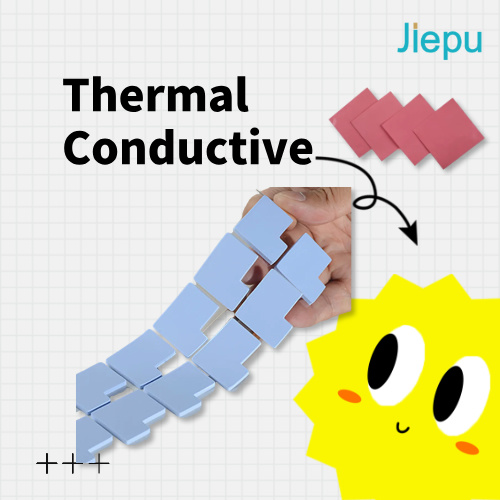
7. Thermal Conductive Materials
What They’re Like: Great at carrying heat away from hot parts.
Examples: Thermal Gap Pads, graphite sheets, thermal gels.
Uses: Cooling electronics and batteries.

8. Conductive Materials
What They’re Like: Conduct electricity, block interference, and bend easily.
Examples: Conductive tapes, Foil Heat Shield, RFI Shielding Tape.
Uses: Grounding electronics and blocking electromagnetic waves.
Comparison of Die-Cutting Materials: Properties and Applications
1. Temperature Resistance Comparison
Let’s compare how well each of these 8 materials handles heat and cold. The table below shows the temperature ranges they can handle:
| Material | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|
| Polyimide Film | -269 to 400 |
| Silicone Rubber | -60 to 250 |
| Polyethylene Foam | -50 to 80 |
| Aluminum Foil | -200 to 660 |
| PET Film | -70 to 150 |
| EVA Foam | -40 to 80 |
| Acrylic Tape | -30 to 120 |
| Copper Foil | -200 to 200 |
What Does This Mean?
Hot Environments: If you need something that works well in high temperatures, Polyimide Film and Aluminum Foil are great choices.
Cold Conditions: For extremely cold environments, Silicone Rubber and Copper Foil perform well without breaking or losing functionality.
2. Flexibility Comparison
Now let’s see how bendy or flexible these materials are. This matters when materials need to be shaped or stretched for different uses.
| Material | Flexibility Rating (1-5) | Where It’s Used |
| Polyimide Film | 4 | Flexible circuits, electrical parts |
| Silicone Rubber | 5 | Cushioning, gaskets |
| Polyethylene Foam | 4 | Packaging, vibration dampening |
| Aluminum Foil | 3 | Heat shields, EMI shielding |
| PET Film | 4 | Labels, laminates |
| EVA Foam | 5 | Sports gear, padding |
| Acrylic Tape | 3 | Bonding, sealing |
| Copper Foil | 2 | Electrical grounding, shielding |
What Does This Mean?
Super Flexible Materials: Silicone Rubber and EVA Foam are great for bending, stretching, and absorbing impact.
Moderately Flexible Materials: Polyimide Film and PET Film work well in many situations where some flexibility is needed.
Less Flexible Options: Copper Foil is stiff and better for stable, non-bendy applications.
3. Adhesive Properties Comparison (For Tapes)
For tape materials, stickiness and how long it lasts are important! Here’s how these tapes compare:
| Material | Stickiness Level | Durability (1-5) | Best Uses |
| Acrylic Tape | High | 4 | Permanent bonding, signs |
| Double-Sided Tape | Medium | 3 | Temporary fixes, prototyping |
| Foam Tape | Medium | 5 | Cushioning, sealing |
What Does This Mean?
Best for Strong Bonds: Acrylic Tape is the strongest and works well for projects where you need things to stay stuck for a long time.
Long-Lasting Durability: Foam Tape can handle wear and tear over time, making it great for sealing and padding.
Quick Fixes: Double-Sided Tape is perfect for short-term solutions and less demanding uses.
4. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Some materials are great at handling heat or carrying electricity. Here’s how they compare:
| Material | Heat Conductivity (W/mK) | Electricity Conductivity (Good/Bad) | Where It Works |
| Polyimide Film | 0.12 | Bad (Insulator) | Circuit protection |
| Silicone Rubber | 0.2-2.0 | Bad (Insulator) | Heat pads, sealing |
| Aluminum Foil | 205 | Good | Heat sinks, EMI shielding |
| Copper Foil | 390 | Excellent | Grounding, EMI shielding |
What Does This Mean?
Best Heat Conductors: Copper Foil and Aluminum Foil are great for spreading heat away from hot spots.
Good for Insulating: Polyimide Film and Silicone Rubber keep heat and electricity from spreading.
Electrical Uses: Copper Foil is the best choice for carrying electricity.
5. Cost Comparison
Finally, let’s look at how much these materials cost. The prices below are for general reference:
| Material | Cost Level | Price Range (USD/kg) | Cost Notes |
| Polyimide Film | High | 50-100 | Expensive but high performance |
| Silicone Rubber | Medium | 10-30 | Versatile and affordable |
| Polyethylene Foam | Low | 2-5 | Budget-friendly for many uses |
| Aluminum Foil | Medium | 5-10 | Great properties at a fair price |
| PET Film | Low | 3-7 | Cost-effective for general uses |
| EVA Foam | Low | 2-4 | Great for cheap, durable padding |
| Acrylic Tape | Medium | 5-15 | Good value for strong adhesives |
| Copper Foil | High | 20-50 | Expensive but excellent conductor |
What Does This Mean?
Best for Tight Budgets: Polyethylene Foam, EVA Foam, and PET Film are the most affordable.
Worth the Price: Polyimide Film and Copper Foil are pricey but deliver excellent performance for special needs.
Balanced Options: Aluminum Foil and Silicone Rubber offer good quality without breaking the bank.
Applications and Market Trends of Die-Cutting Materials
Applications in Different Industries
Die-cutting materials are used in many areas because they are strong, flexible, and useful. Here are some examples:
Electronics: Die-cutting materials help make wireless chargers by creating inductive coils. These materials are great at carrying electricity and spreading heat, which makes devices work better.
Medical: In healthcare, these materials are used for things like bandages, seals, and medical devices. Silicone rubber and PET film are often chosen because they are safe for the body and last a long time.
Automotive: Cars need materials that can handle high heat and last a long time. For example, polyimide film is used in car sensors, and EVA foam is used for cushioning and reducing noise.
Home Appliances: Die-cutting materials like aluminum foil and copper foil help ovens keep heat in and stop interference in smart appliances.
New Uses: Die-cutting materials are also being used in cool new technologies like foldable screens, fitness trackers, and electric car batteries. These uses need materials that are flexible, lightweight, and advanced.
Market Trends Shaping the Future
The market for die-cutting materials is changing to focus on eco-friendly and modern solutions. Here are some trends:
Going Green:
More industries are using materials that can break down naturally or be recycled, like biodegradable foam and tapes made from plants.
Factories are also finding ways to save energy and create less waste.
Electronics and Electric Cars:
Electric cars need materials like copper foil, which carry heat and electricity well, to make their batteries and parts work efficiently.
As 5G and smart devices grow, there’s a big need for die-cut materials that can handle new challenges.
Light and Strong Materials:
Car and airplane makers want lighter materials, like polyimide film and PET film, to save fuel and costs while still being tough.
Custom Designs:
Companies want die-cut materials made to fit their exact needs, so technologies like laser cutting are becoming more popular.

Die-cutting materials are used in so many things, from gadgets to cars and healthcare. In the future, using eco-friendly, lightweight, and high-tech materials will be very important. Paying attention to these trends will help businesses stay ahead in a changing world.
Whether you’re a student curious about how everyday objects are made or an industry professional exploring new materials, understanding the role of die-cutting materials can open up new opportunities. The next time you see a sleek electronic device or step into a quiet car, remember the unseen materials that make it all possible!
At Jiepu, we specialize in providing die-cutting services for all the materials mentioned above. If you have any needs or questions, feel free to contact us—we’re here to help!



