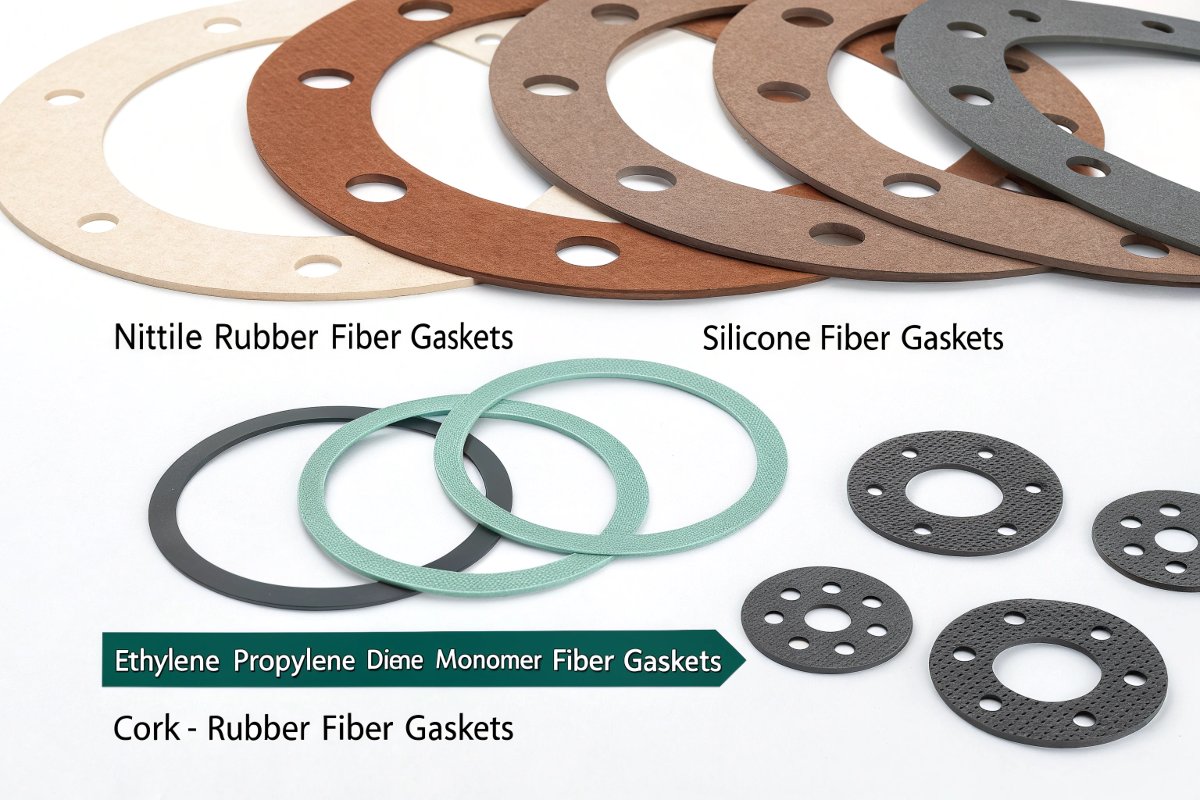
Hello, let’s talk about something truly tremendous today—fiber gaskets in die-cutting.
Now, I know what you’re thinking: “Mark, why should I care about fiber gaskets?”
Well, let me tell you, these little components are the unsung heroes of many industries, ensuring everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
So, let’s dive into the world of fiber gaskets, exploring their materials, properties, applications, and some industry insights.
1. NBR (Nitrile Rubber) Fiber Composite Gaskets

Material Composition:
Base Material: Nitrile rubber, known for its excellent oil resistance.
Reinforcement: Fibers like cellulose or aramid to enhance structural integrity.
Properties:
Oil Resistance: Ideal for environments with fuels and lubricants, making them the top choice for automotive and machinery sectors.
Elasticity & Compression Resilience: Provides stable sealing performance, adapting to dynamic pressure changes.
Temperature Range: Operates effectively between -40°C to +120°C, with short-term tolerance up to 150°C.
Application Scenarios:
Sealing under car hoods.
Gaskets in fuel system pipelines.
Seals in hydraulic equipment.
Industry Insights:
Advantages: Cost-effective and easy to die-cut, suitable for mass production.
Limitations: Not resistant to ozone or UV light; prolonged exposure requires surface treatments.
2. Silicone Fiber Composite Gaskets
Material Composition:
Base Material: Silicone rubber.
Reinforcement: Glass or polyester fibers.
Properties:
Temperature Resistance: From -60°C to +230°C; food-grade silicone meets FDA standards.
Chemical Inertness: Resistant to acids, alkalis, ozone, and UV light, perfect for outdoor and medical applications.
Flexibility: Low compression set, excellent adaptability to sealing surfaces.
Application Scenarios:
Food processing equipment.
Medical device seals.
LED lighting insulation pads.
High-temperature pipeline flanges.
Industry Insights:
Trend: The medical and food industries are moving towards platinum-cured silicone due to its non-toxic residues.
Challenges: Lower mechanical strength necessitates fiber reinforcement to improve tear resistance.
3. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Fiber Gaskets

Material Composition:
- EPDM rubber combined with cellulose or synthetic fiber framework.
Properties:
Weather Resistance: Excellent resistance to ozone and UV aging, suitable for long-term outdoor use.
Water Resistance: Low water absorption, ideal for humid environments like cooling systems.
Temperature Range: Effective between -50°C to +150°C.
Application Scenarios:
Seals in building doors and windows.
Cooling tower flange gaskets.
Marine equipment seals.
Industry Insights:
Advantages: High cost-performance ratio, an eco-friendly alternative to traditional asbestos gaskets.
Limitations: Not resistant to mineral oils; avoid contact with gasoline or diesel environments.
4. Cork-Rubber Composite Fiber Gaskets
Material Composition:
- Natural cork particles bonded with synthetic rubber (like SBR) and reinforced with fiber mesh.
Properties:
Vibration Damping: Cork structure absorbs vibrations, reducing noise better than pure rubber.
Compressibility: Adapts to uneven flange surfaces, excellent gap-filling capabilities.
Eco-Friendliness: Natural cork is renewable, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Application Scenarios:
Industrial equipment vibration-damping bases.
Pipeline flange seals.
Furniture anti-slip pads.
Industry Insights:
Trend: Used in electric vehicle battery packs for vibration damping, meeting lightweight requirements.
Challenges: Cork particles may crack under prolonged high-pressure; regular replacement is necessary.
5. Aramid Fiber (Kevlar) Reinforced Gaskets
Material Composition:
- Aramid fiber (like Kevlar) woven layers combined with high-temperature-resistant resin or rubber matrix.
Properties:
High Strength: Exceptional tensile and cut resistance, similar to bulletproof materials.
High-Temperature Resistance: Continuous use up to 300°C, suitable for aerospace and military applications.
Low Thermal Conductivity: Ideal for high-temperature insulation scenarios.
Application Scenarios:
Aerospace engine seals.
High-temperature valve gaskets.
Explosion-proof equipment seals.
Industry Insights:
Advantages: A lightweight alternative to metal gaskets, reducing equipment weight.
Cost: High material costs limit usage to high-end manufacturing fields.
6. Cellulose Fiber Gaskets

Material Composition:
- Base Material: Plant-based fibers, such as wood pulp and cotton, infused with resin.
Properties:
- Biodegradability: 100% eco-friendly and recyclable, making it a sustainable choice.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The most affordable option, perfect for low-pressure and low-temperature environments.
Application Scenarios:
- Packaging industry cushioning pads – used for sealing and shock absorption in transportation.
- Low-pressure water pipe seals – effective for short-term or temporary applications.
- Temporary repair gaskets – a quick and easy fix for minor leaks.
Industry Insights:
- Limitations: Cellulose gaskets absorb water and swell over time, reducing their durability.
- Use Case Consideration: Best suited for applications where frequent replacement is acceptable.
Key Selection Factors for Fiber Gaskets
Choosing the right gasket is crucial. Here’s what you should consider:
| Factor | Best Material Choices |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Aramid (Kevlar), Silicone, EPDM |
| Oil & Fuel Resistance | NBR, Cork-Rubber Composite |
| Water & Moisture Resistance | EPDM, Silicone |
| High-Pressure Tolerance | Aramid (Kevlar), NBR |
| Flexibility & Softness | Silicone, Cork-Rubber |
| Eco-Friendly & Biodegradable | Cellulose, Cork-Rubber |
Optimizing Die-Cutting for Fiber Gaskets
Die-cutting these gaskets isn’t just about slicing and dicing—precision is everything. If you want top-notch results, here are some tips:
1. Tool Selection Matters
- Harder materials (like Aramid) require carbide blades to prevent fraying.
- Softer materials (like Cork & Cellulose) work best with steel-rule dies for clean cuts.
2. Adhesive Compatibility
- Silicone gaskets need silane coupling agents for effective bonding.
- NBR gaskets work well with epoxy-based adhesives.
3. Multi-Layer Gasket Cutting
- For composite gaskets (e.g., Aramid + Silicone), precision alignment is critical to avoid material waste.

